Devuan-Simple
Devuan ISO Step-by-Step Installation
In this tutorial we're gonna see how to install 'Devuan OS' as guest in OpenBSD host server. This tutorial covers the following topics:
1. Downloading and Verifying the Devuan ISO.
2. Installing Devuan ISO and GRUB.
3. Modifying GRUB configuration.
4. Setting up Cronjob for stable internet connectivity.
5. Setting up Static IP Address.
1. Downloading and Verifying the Devuan ISO
$ ftp https://mirror.leaseweb.com/devuan/devuan_beowulf/installer-iso/devuan_beowulf_3.1.1_amd64_netinstall.iso $ ftp https://mirror.leaseweb.com/devuan/devuan_beowulf/installer-iso/SHA256SUMS $ ftp https://mirror.leaseweb.com/devuan/devuan_beowulf/installer-iso/SHA256SUMS.asc
If gpg is not already installed:
$ doas pkg_add gnupg
$ gpg --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys E93D7167A4F5FA9E9FED497770285BA5CF280BA4 gpg: key 70285BA5CF280BA4: public key "Ralph Ronnquist (rrq) <ralph.ronnquist@gmail.com>" imported gpg: Total number processed: 1 gpg: imported: 1 $ gpg --verify SHA256SUMS.asc SHA256SUMS gpg: Signature made Fri Mar 26 17:50:56 2021 CDT gpg: using RSA key E93D7167A4F5FA9E9FED497770285BA5CF280BA4 gpg: Good signature from "Ralph Ronnquist (rrq) <ralph.ronnquist@gmail.com>" [unknown] gpg: WARNING: This key is not certified with a trusted signature! gpg: There is no indication that the signature belongs to the owner. Primary key fingerprint: E93D 7167 A4F5 FA9E 9FED 4977 7028 5BA5 CF28 0BA4 $ sha256 devuan_beowulf_3.1.1_amd64_netinstall.iso SHA256 (devuan_beowulf_3.1.1_amd64_netinstall.iso) = 1723cbbeb1aee26a54e1370b688e7dc03921402348d2a60086c58c18cd9cf24b $ grep devuan_beowulf_3.1.1_amd64_netinstall.iso SHA256SUMS 1723cbbeb1aee26a54e1370b688e7dc03921402348d2a60086c58c18cd9cf24b devuan_beowulf_3.1.1_amd64_netinstall.iso
The two checksums must match perfectly or else you should stop installation.
2. Installing the Devuan ISO
Before we dive into installation, make sure that you updated the cdrom image in VMM.
VMM
In /etc/vm.conf, we update the cdrom image:
(Make sure the path is correct)
vm "username" {
owner username
memory 1024M
cdrom "/home/iso/devuan-beowulf-3.1.1-vmm.iso"
disk /home/username/username.qcow2
interface {
locked lladdr aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff
switch "switch0"
}
}
Now, we're gonna install the ISO, Run the following commands, $ doas vmctl reload $ doas vmctl stop "username" $ doas vmctl start -c "username"
the reload command reloads the vm.conf and starts the machine, going into console after that might be okay for other OS distributions, but in Devuan it will stuck at select video size. so after reloading, stop and start into console mode directly.
Note: the "username" mentioned above is the vm "username" in /etc/vm.conf for the machine.
Warning: After the "doas vmctl start -c "username"" command, DO NOT press Enter key more than once. ( If you do, then you have to restart VPS again to get the installation screen as the image below). 
Press TAB and edit menu entry add "console=ttyS0,115200n8" (without quotes) as shown in the picture
below and press Enter 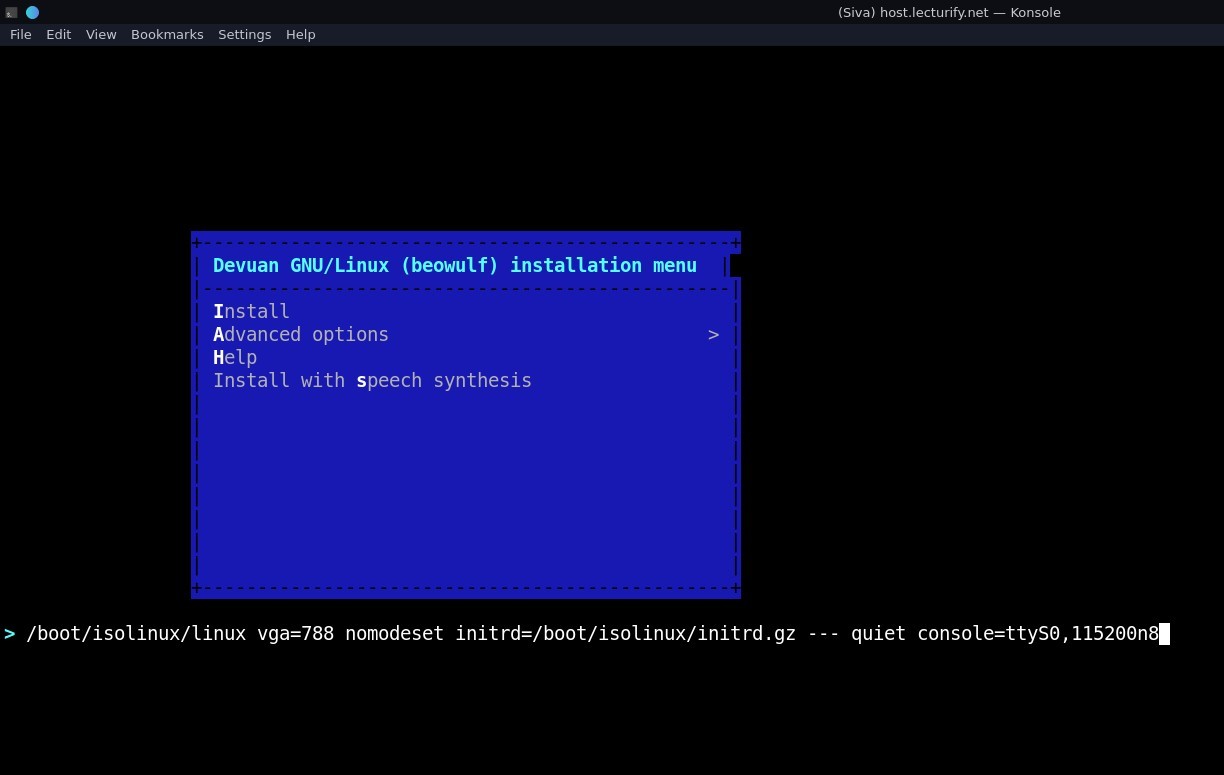
The installer will open, it might be bit glitchy while rendering but give it a second it'll show the screen as follows:
Note: the installer window won't be shown fullscreen (unless your Monitor resolution is small), the images shown below are cropped. 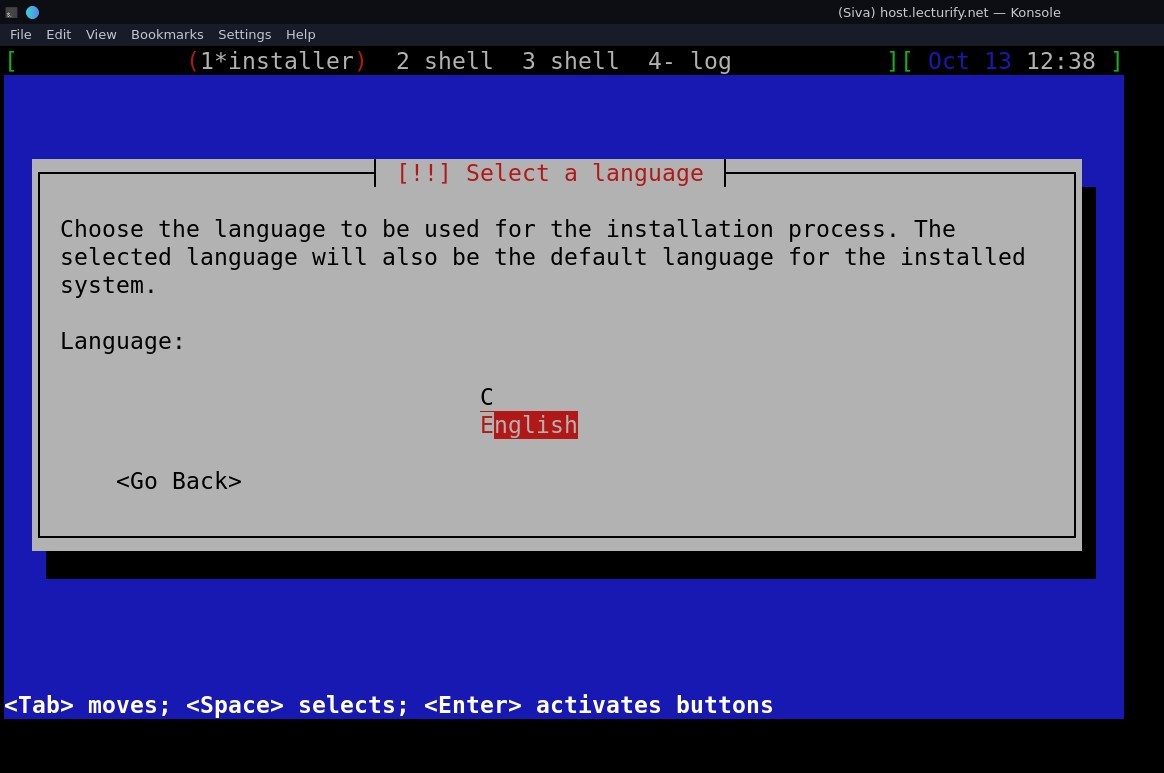
Select language and press Enter
and the next step, select keyboard configuration (see pic below)
After that the installer configures network with DHCP "Do Not Press Enter" as it cancels (see pic below) 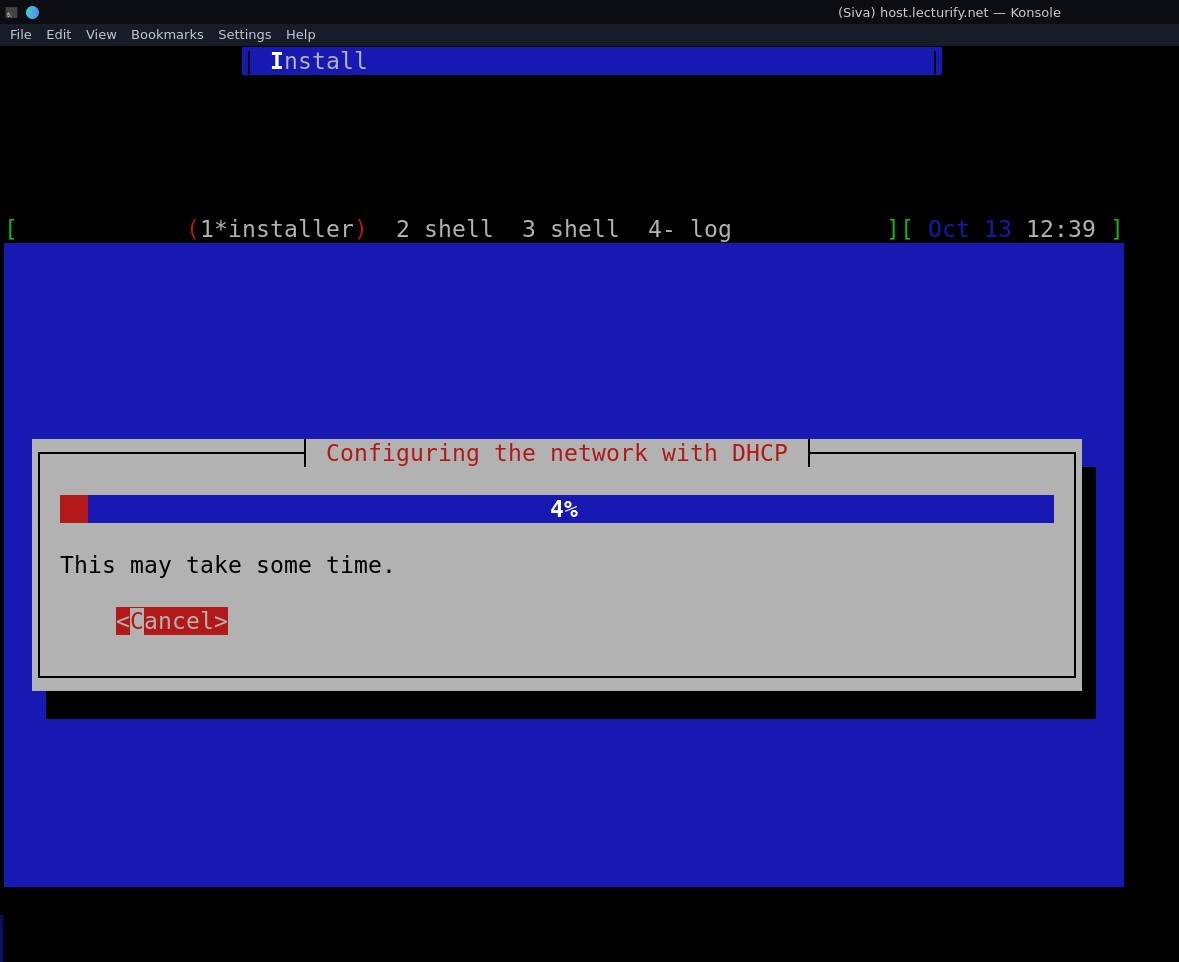 and then enter "hostname" "domain name" and "root password" (see pics below for reference)
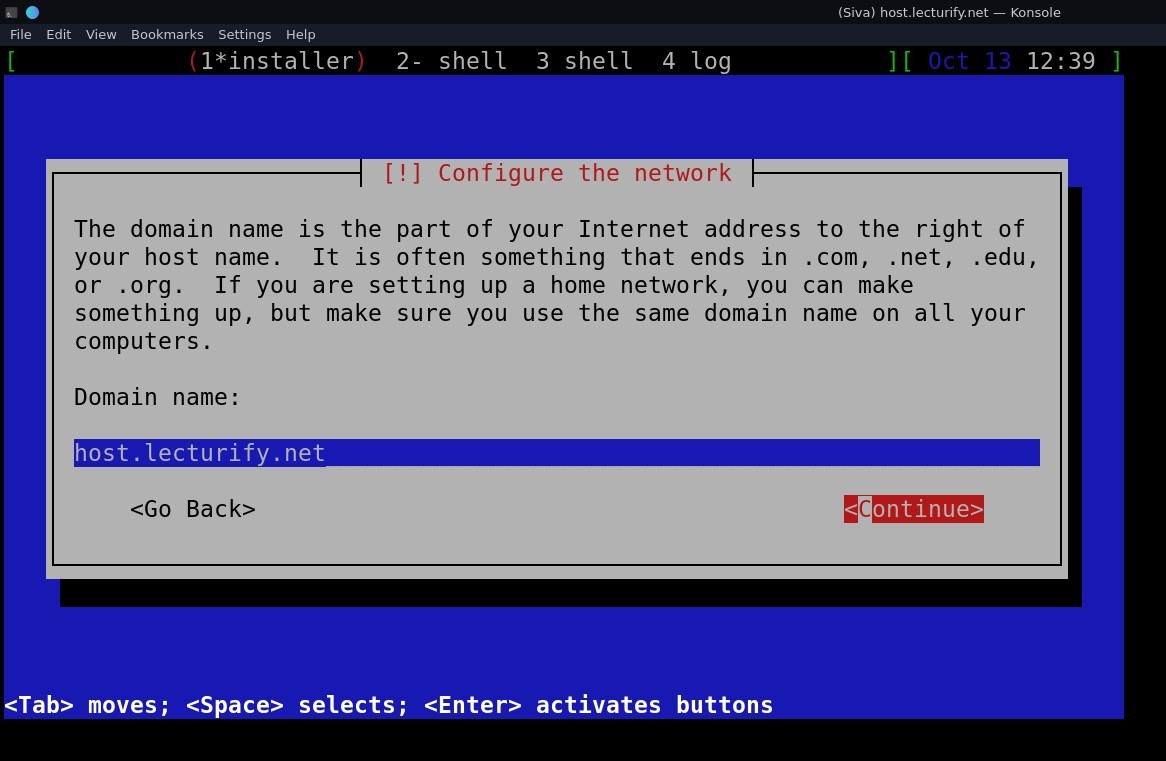
and then enter "hostname" "domain name" and "root password" (see pics below for reference) 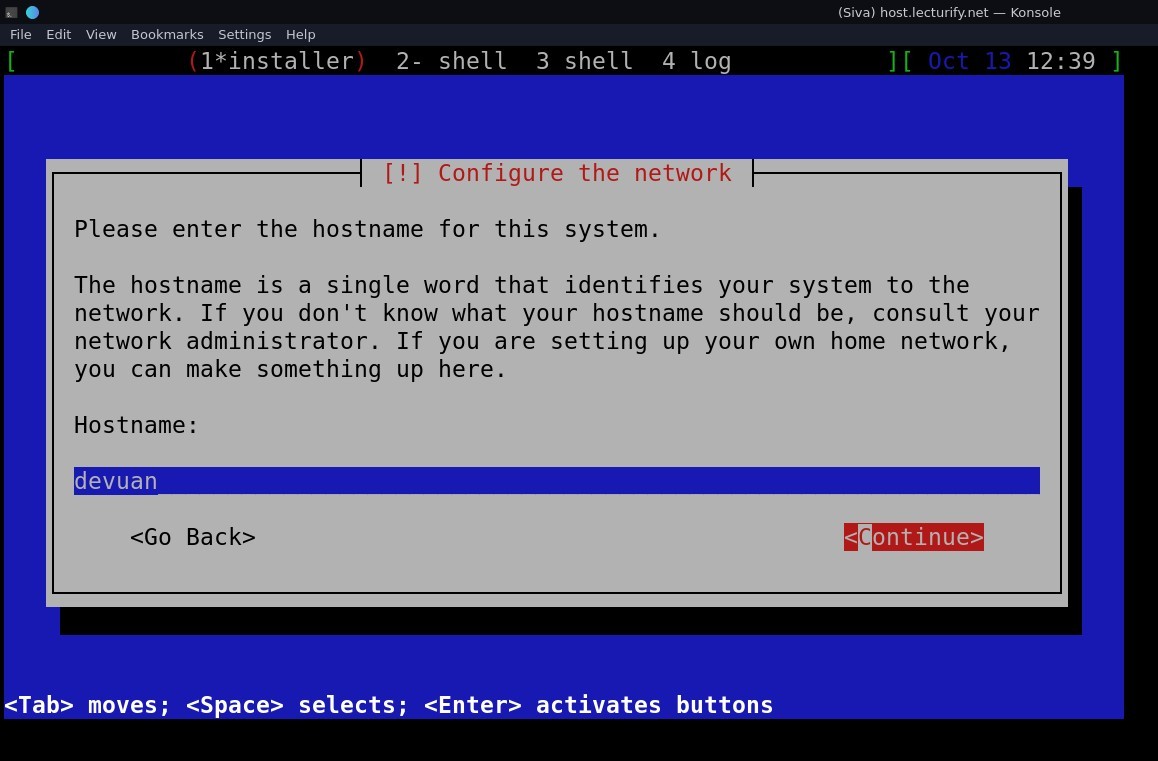
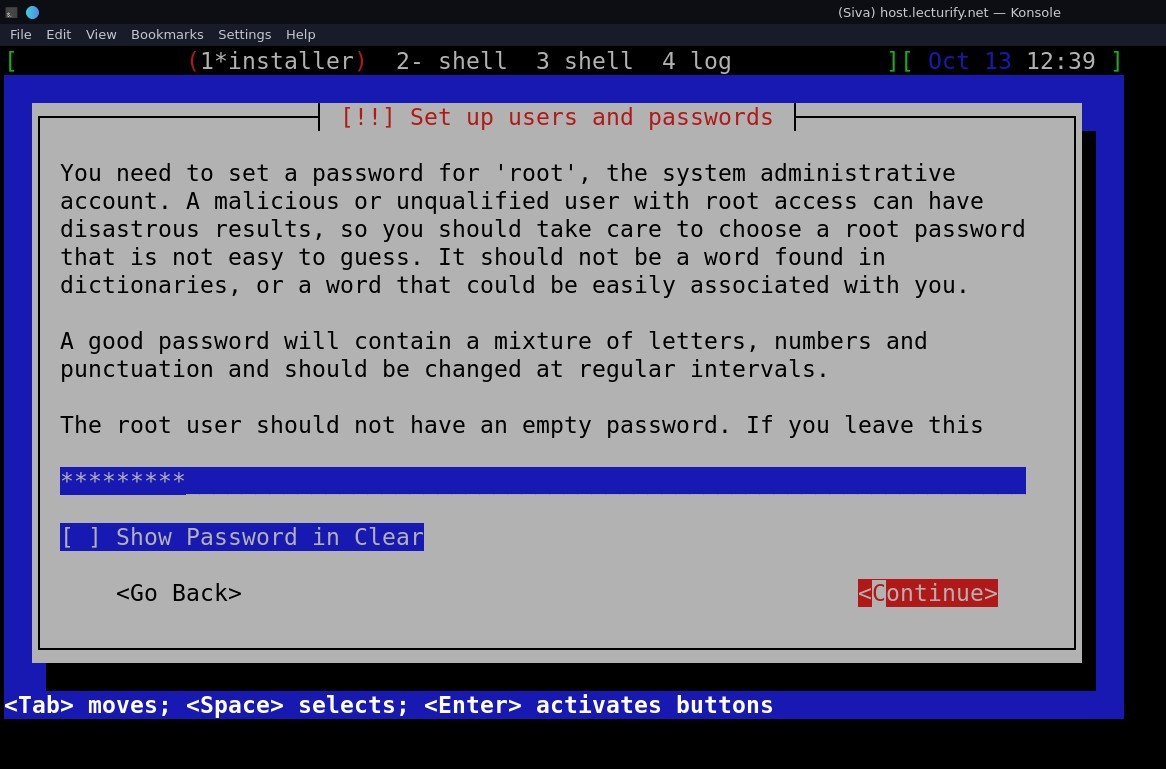
next is user setup, you can add a user and password. (when setting up passwords, it asks for confirmation password where you have to enter same password again. The pic below only shows the username screen, enter your desired username and followed by password).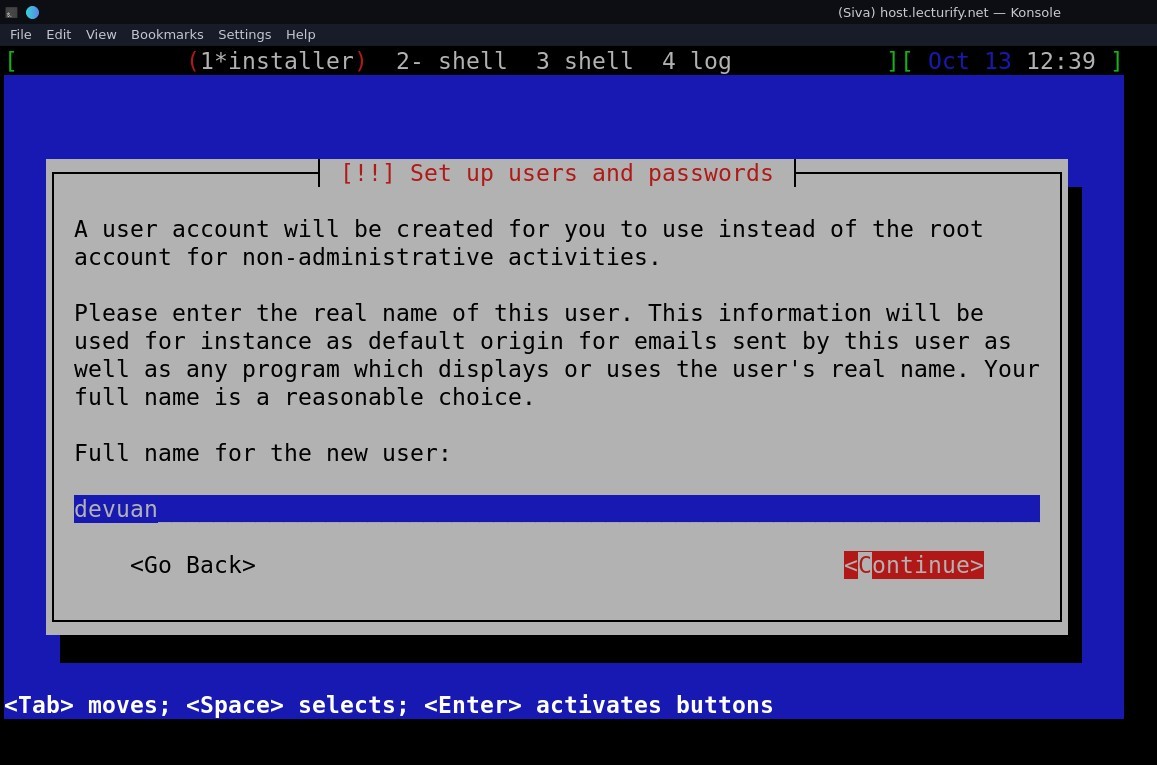
once done, you'll be prompted to configure the clock, choose the timezone from the list and continue 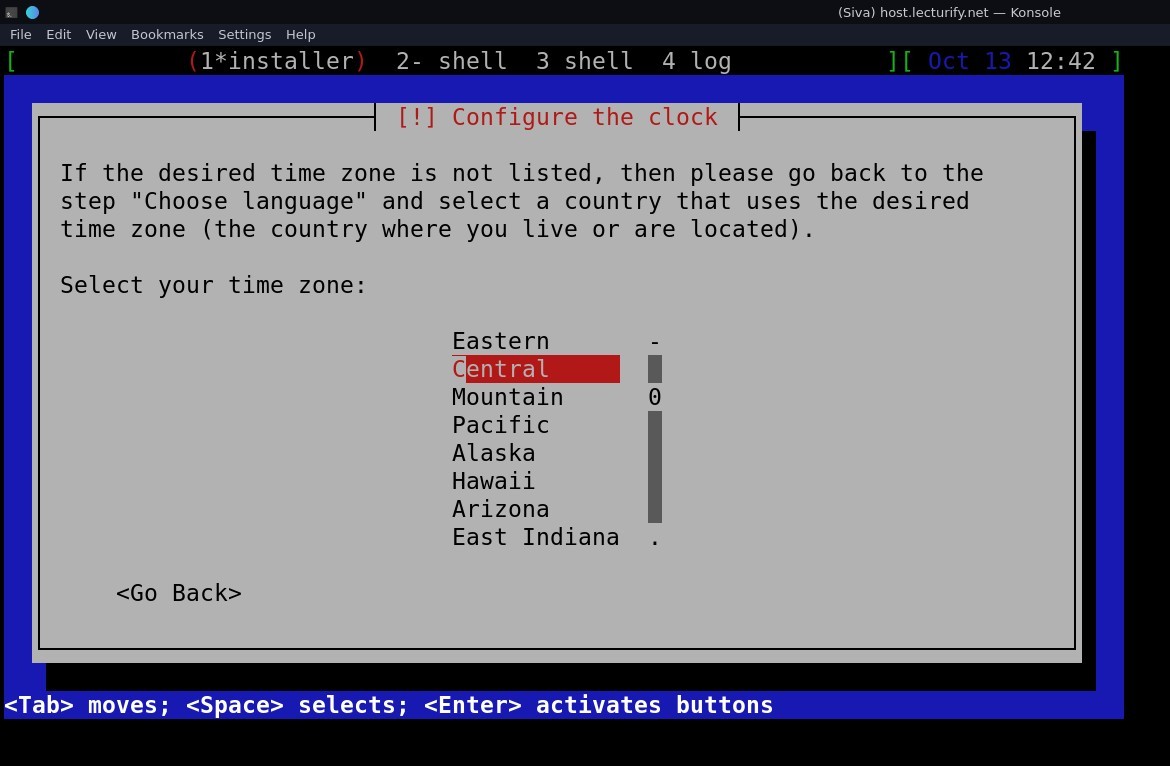
The next step is disk partitioning 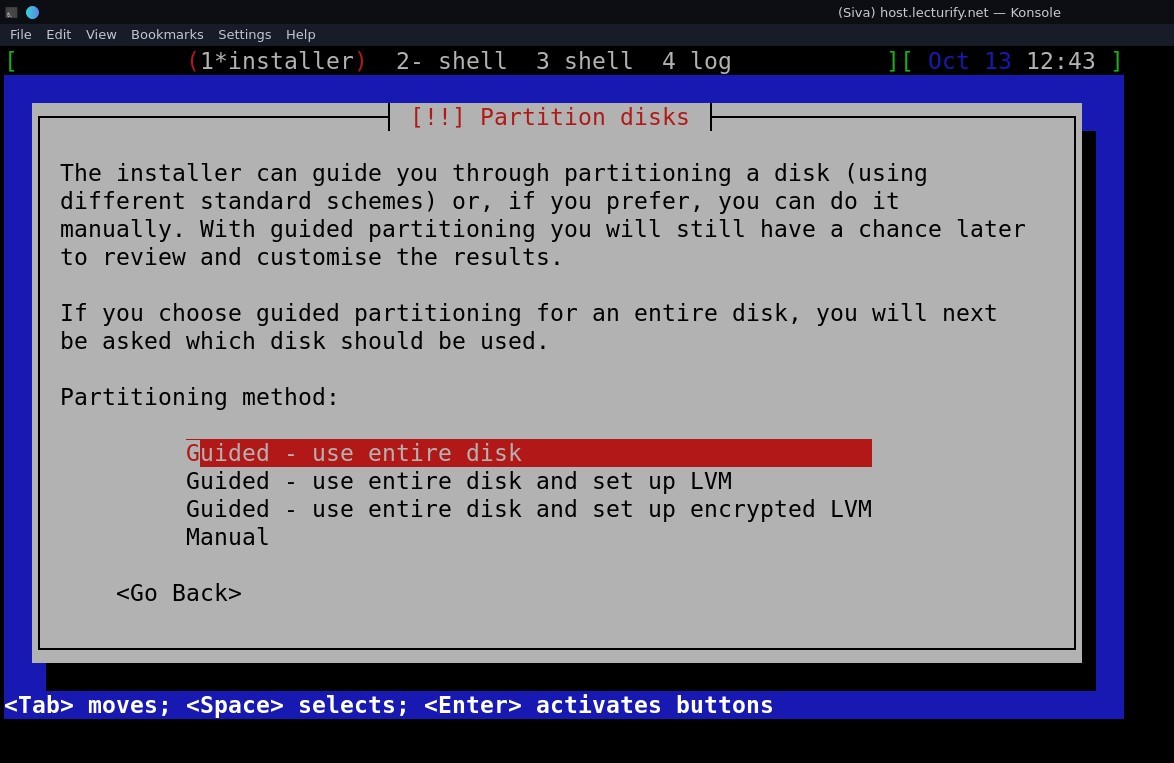
I used "Guided - use entire disk" option for partitioning method.
and select disk for partitioning, we have only option "Virtual disk 1 (vda), press Enter
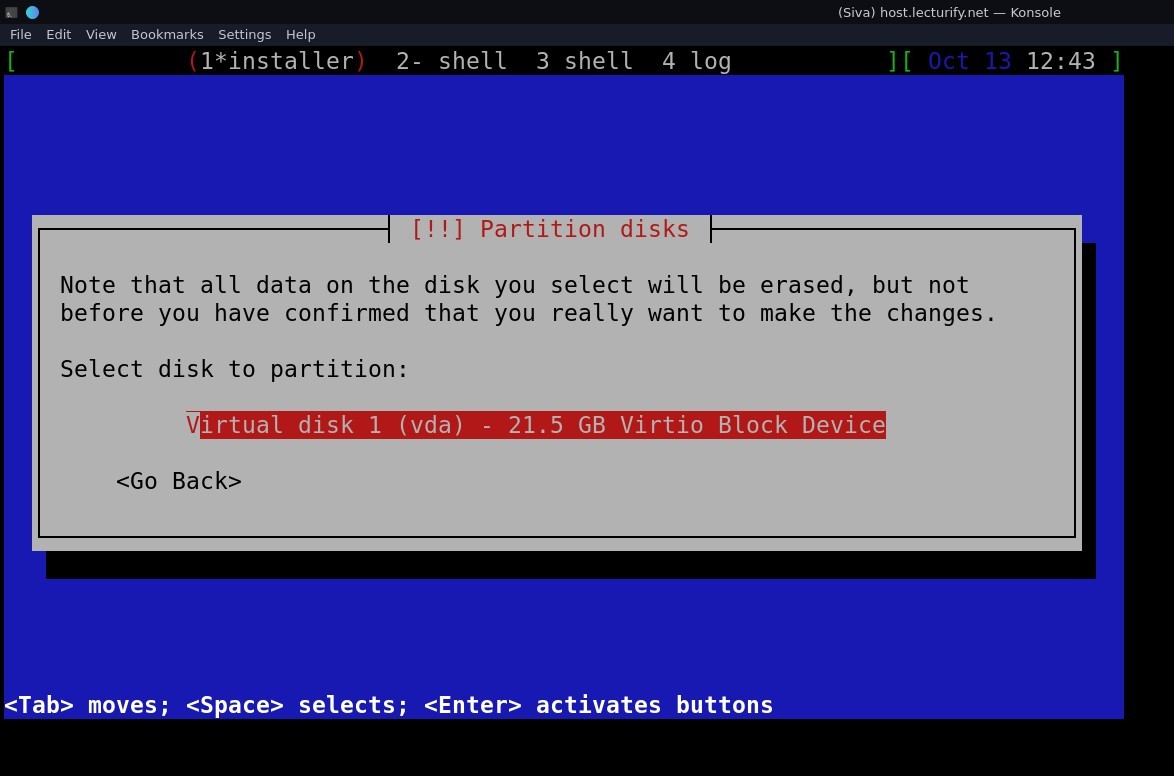
after that, select partitioning scheme (see pic below) 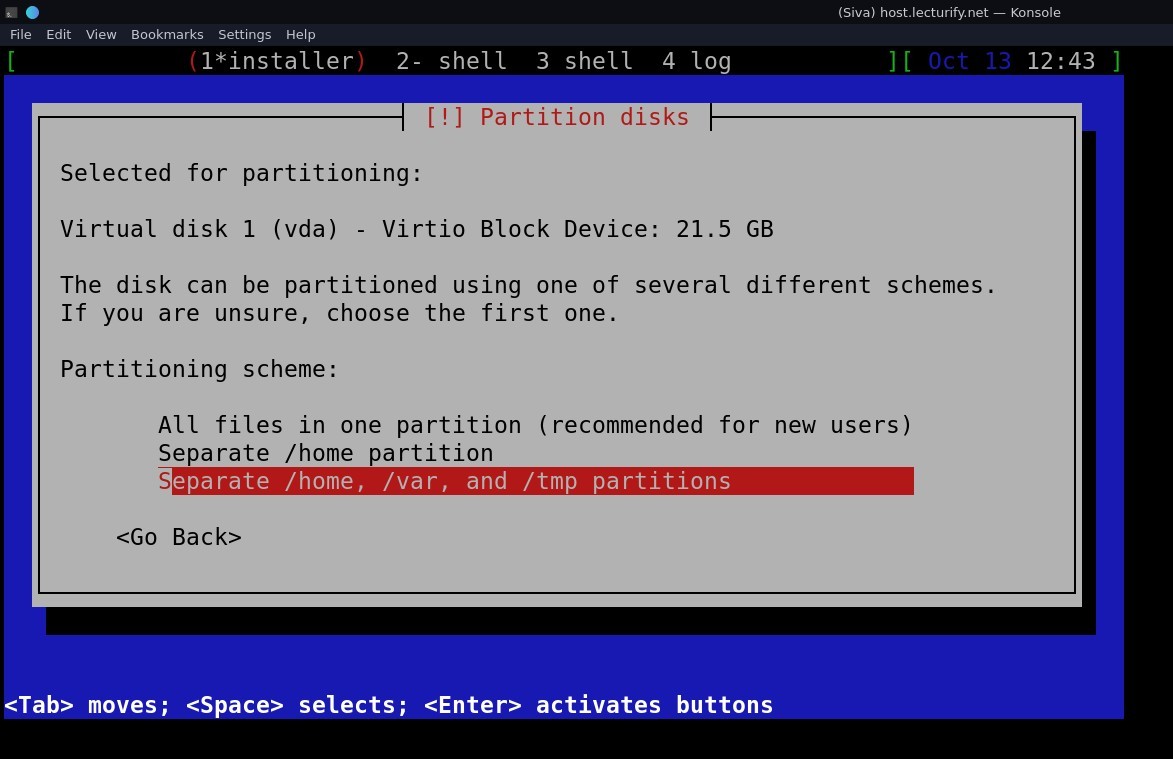
I choose seperate /home,/var and /tmp partitions, you can choose as per your use.
It displays the disk partitions, select "Finish partitioning and write changes to the disk. 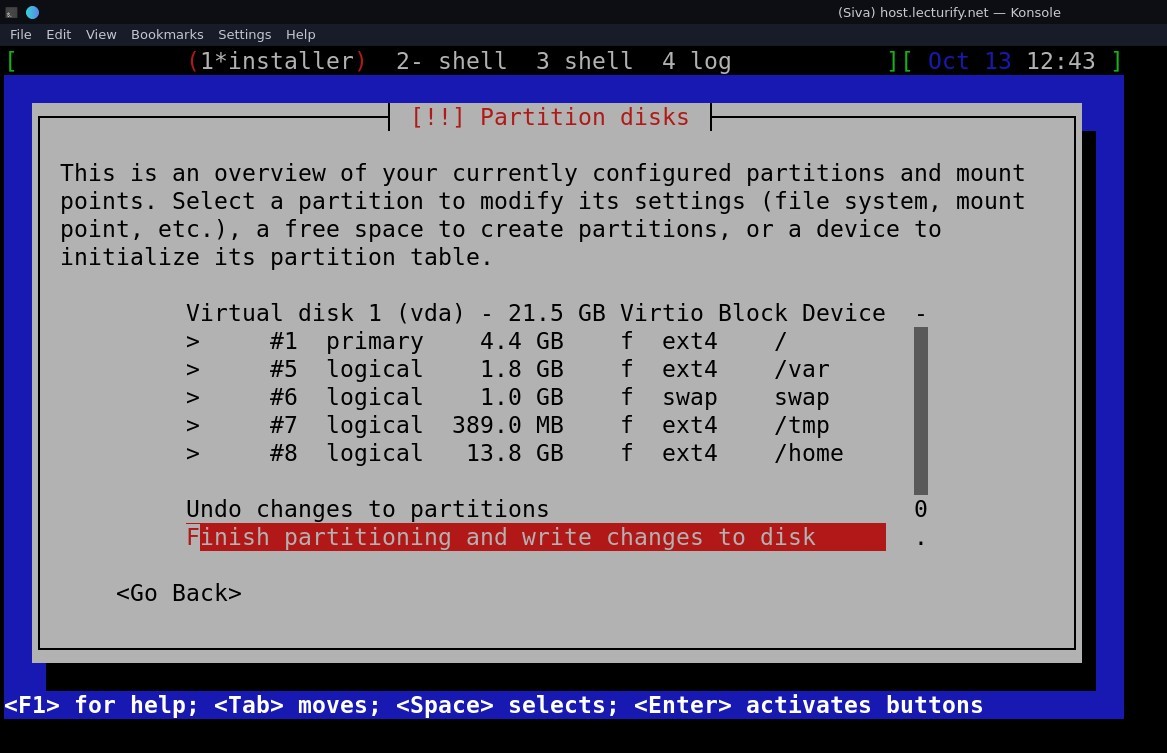
again, it asks for confirmation "write changes to the disk" select "yes" and press enter. 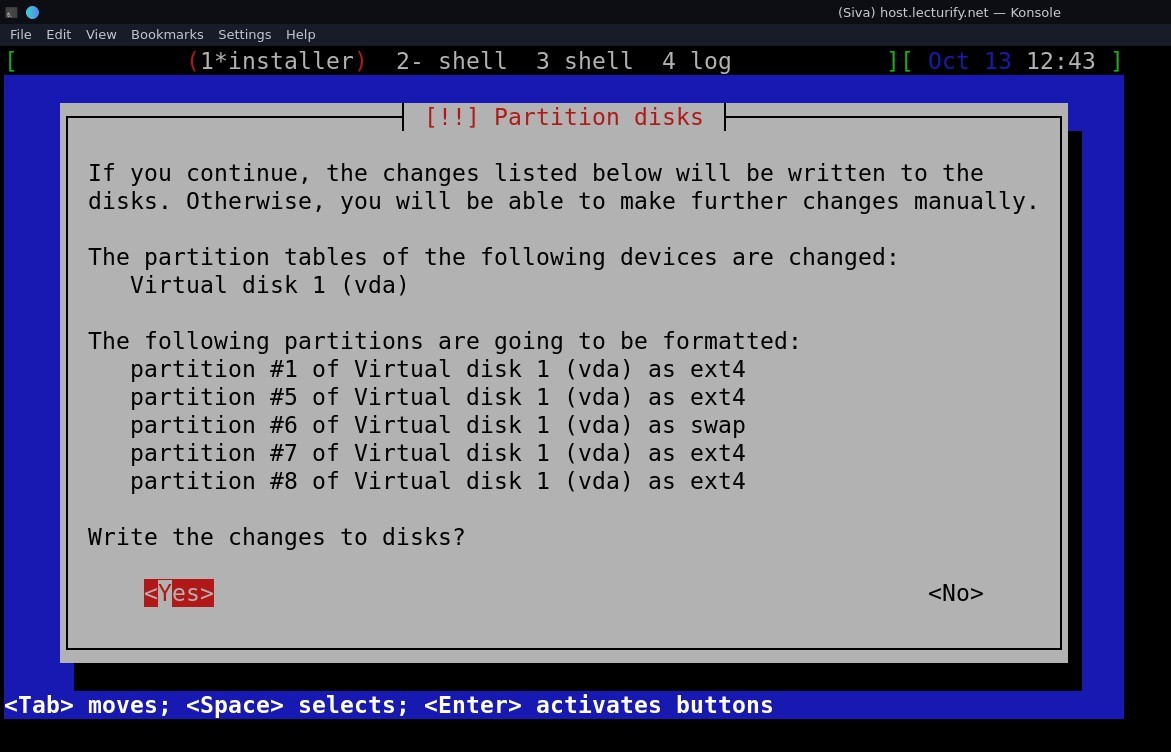
wait until it installs the base system. 
now, the configuration package manager scans the 'cd or dvd' and shows our installation image, and asks you whether to scan another CD or DVD, select "NO" and press enter.
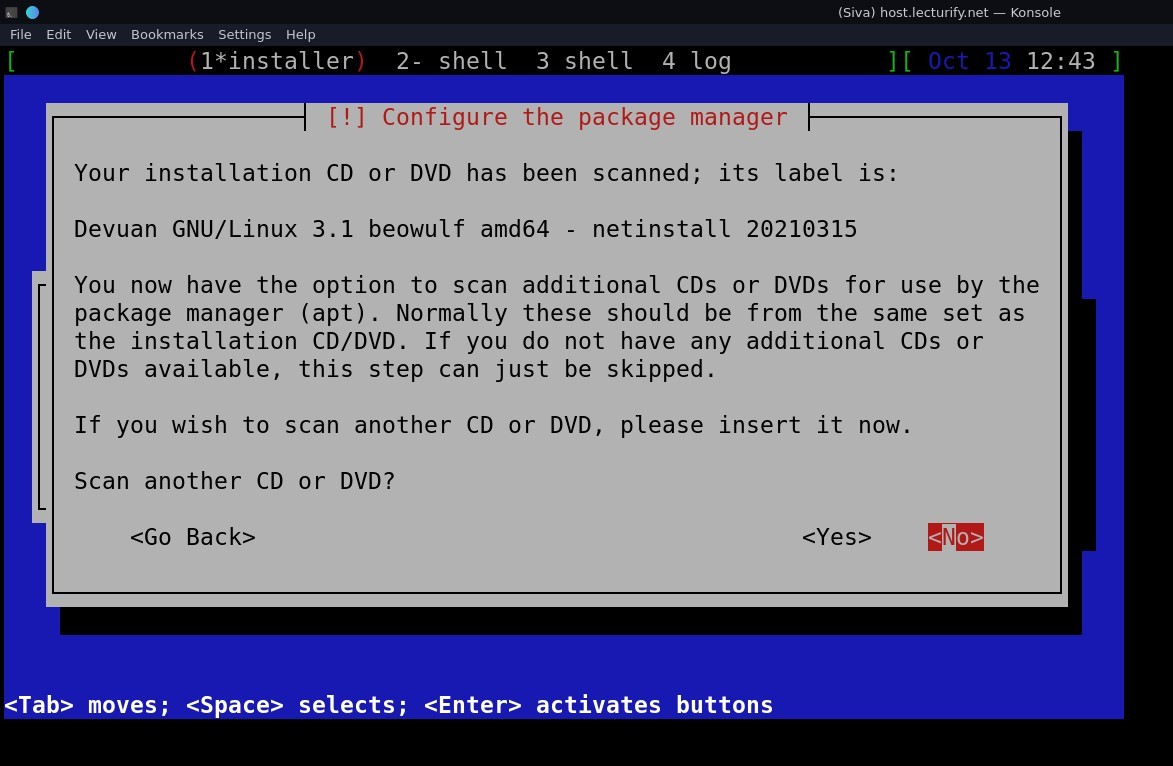
then select the Devuan archive mirror from the list (see the pic), select and press enter
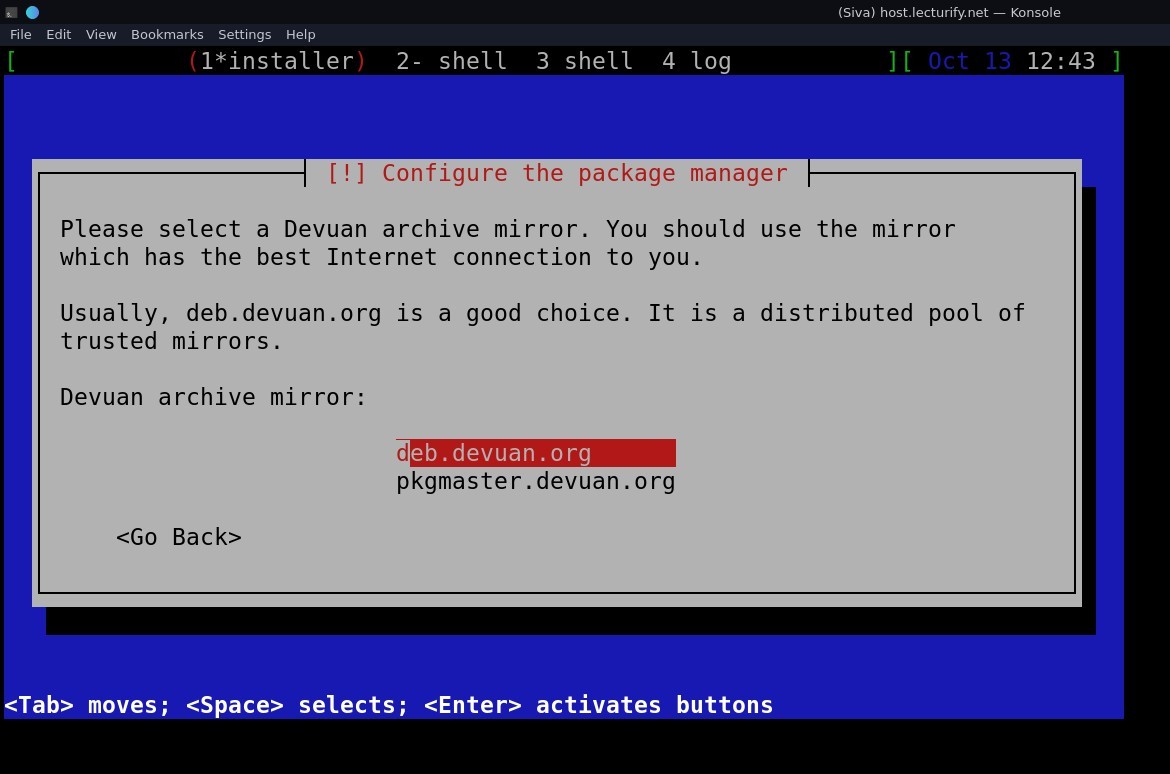
you can setup proxy if you have any, in our case we don't use, so select continue and press enter.
after that, you have to wait until the two process finish (see the following pics)
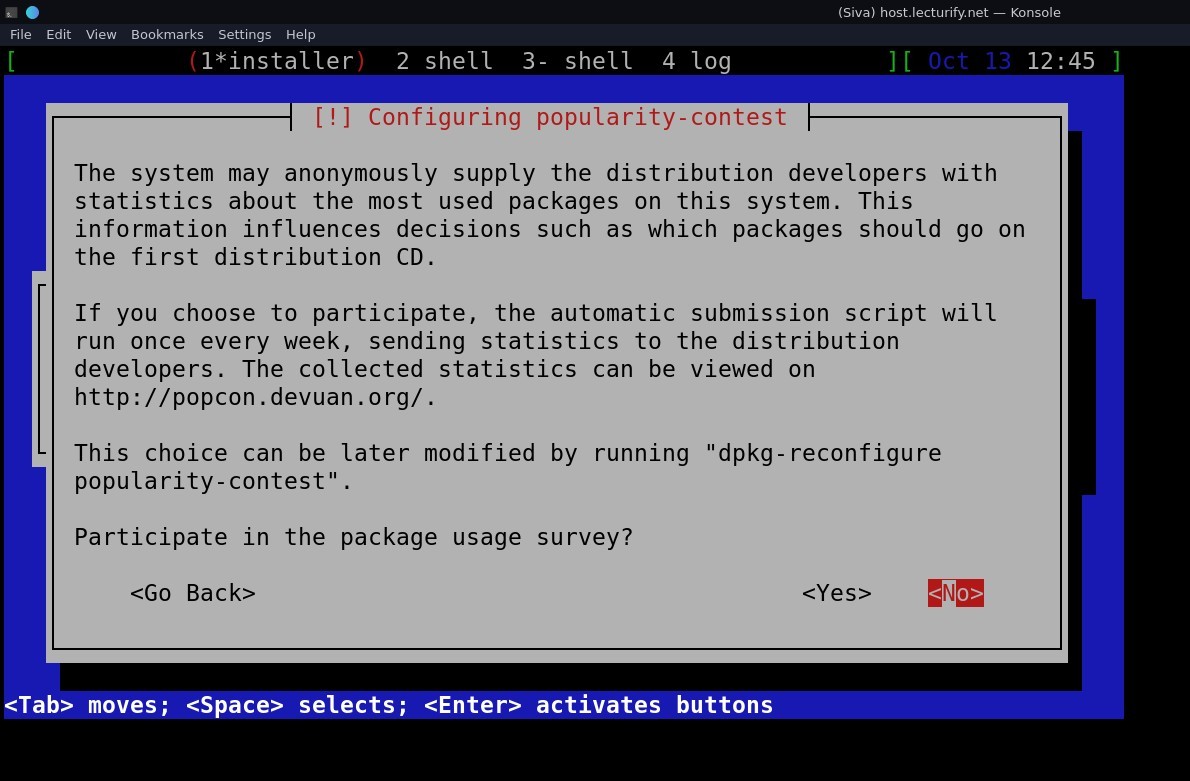
the next step it asks for "Participate in pakcage usage survey" , I choose 'NO'
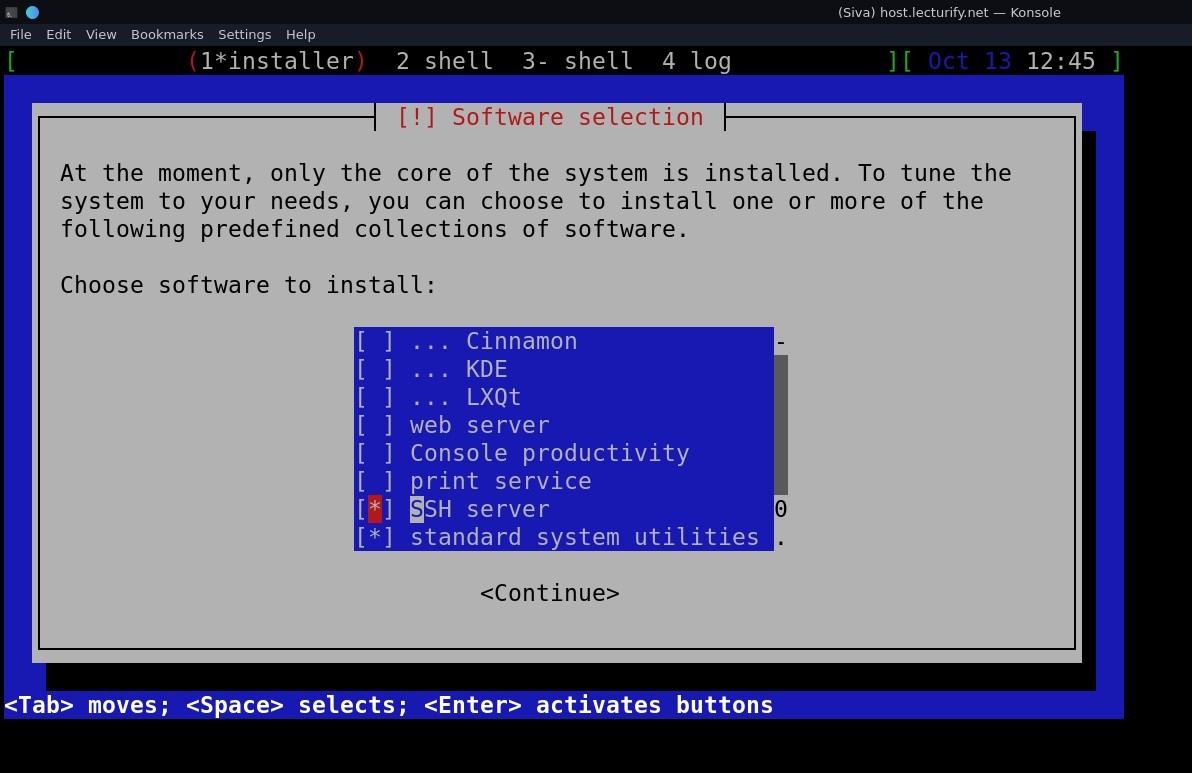
and the you have to select Desktop Environments, as we only have serial console support, just scroll the menu and choose "SSH Server and Standard system utilities.
Note: By default "Standard system utilities is marked, you only have to mark "SSH Server" and select "Continue" and press enter.
The next step is important make sure you read and understand the information shown (see pic below)
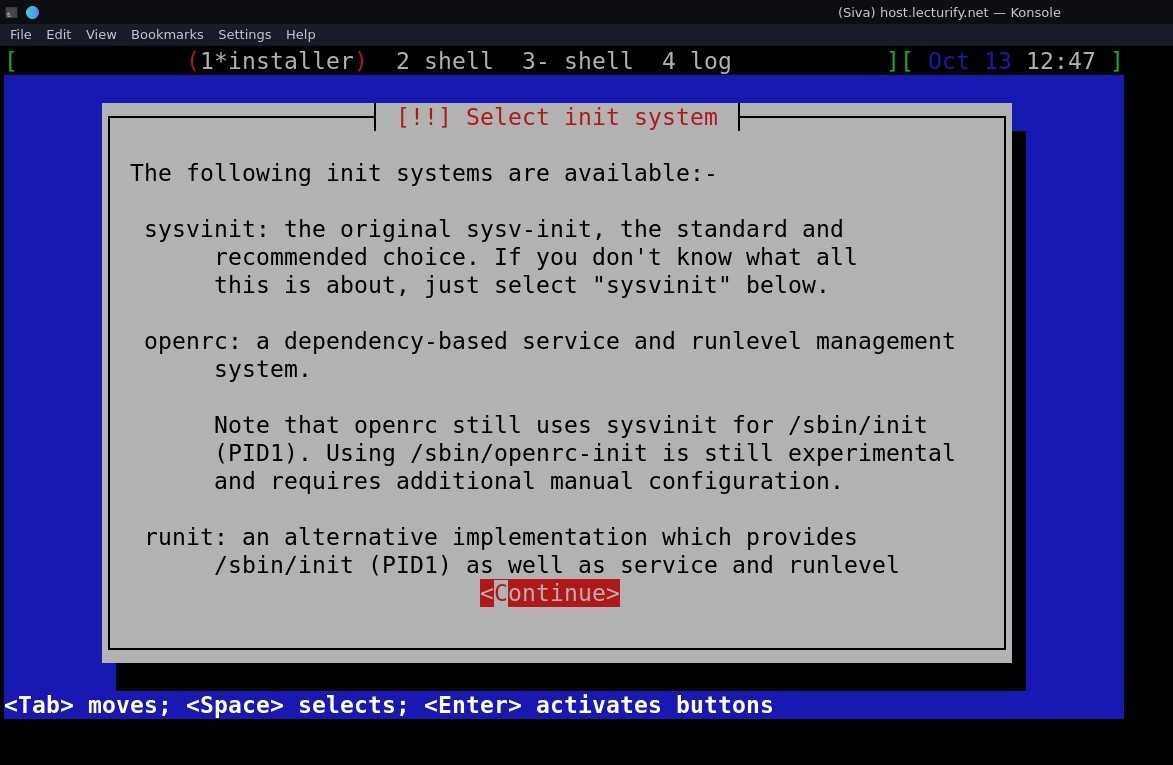
I selected here the original "sysvinit" , you can choose as per your needs. But, if you choose other methods, the commands we use later in this tutorial might not work as yours using a different "init", still you can follow this tutorial, just replace the commands as per your system needs.
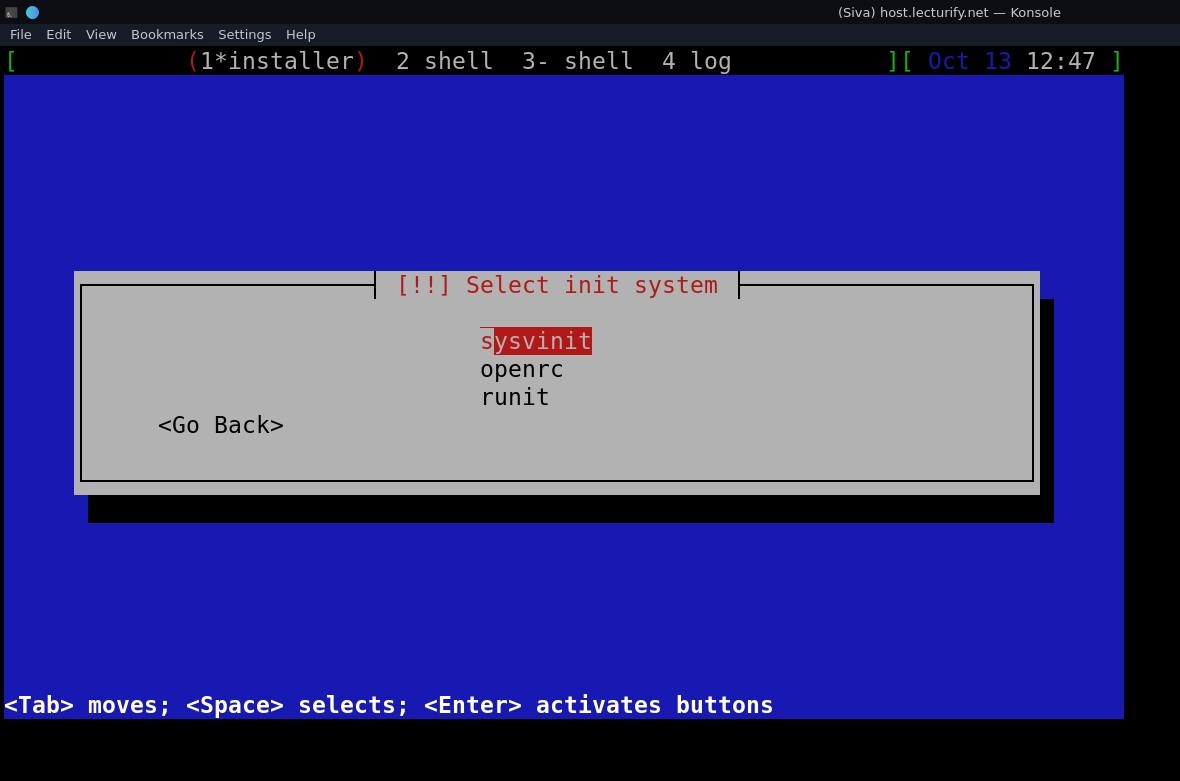
Next step is GRUB Installation, Select "Yes" and press enter for "Install the GRUB Boot loader to master boot record" and select device "/dev/vda" for bootloader installation (see the following pics) 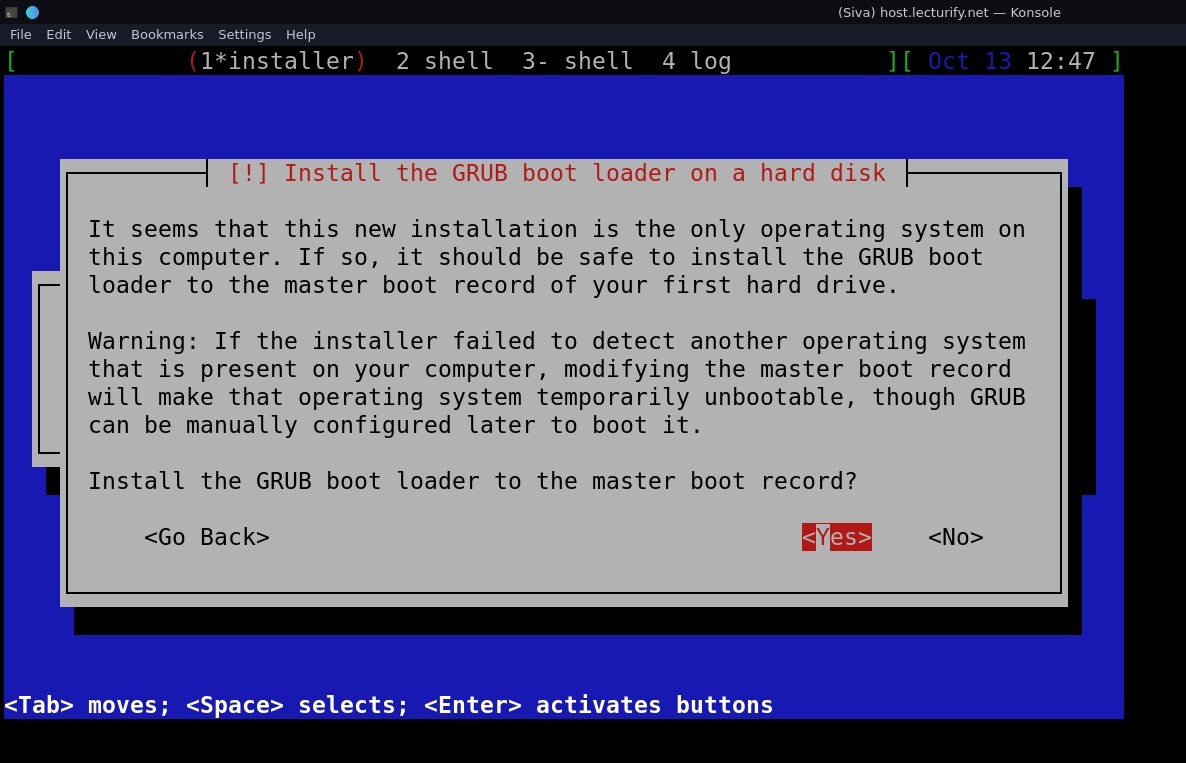
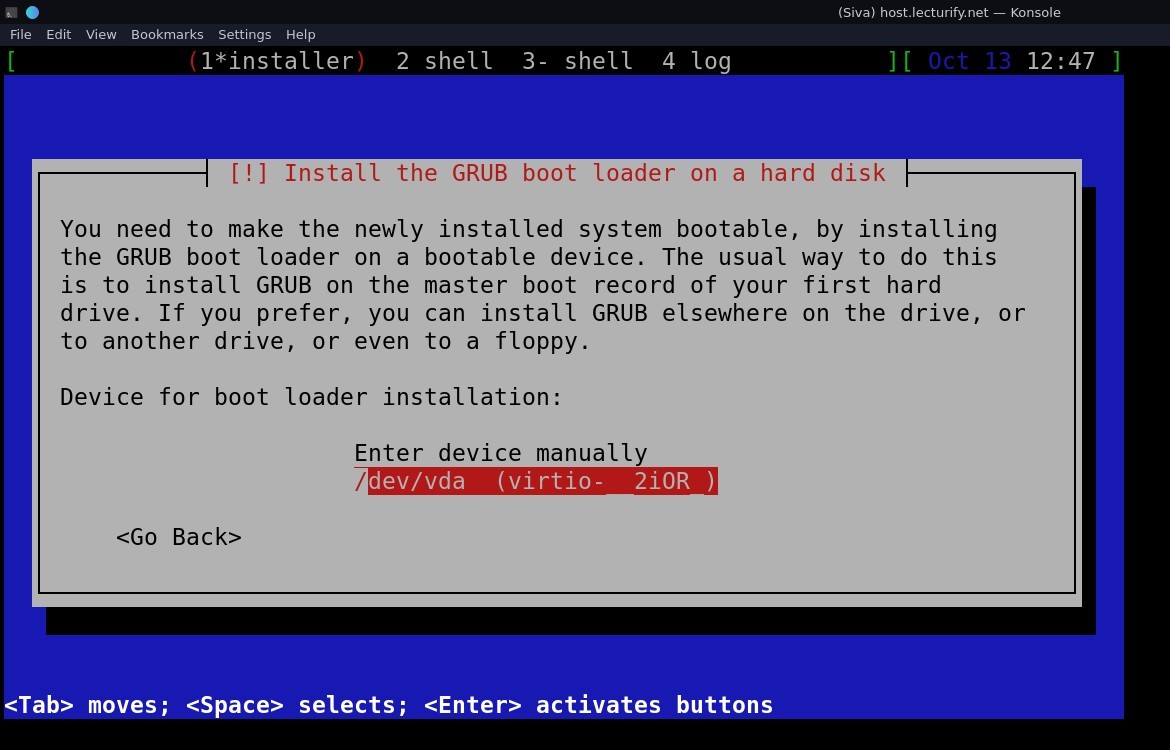
and the installation complete dialogue is shown, select "continue" and press enter, the system will reboot.
you might see some glitches on screen 
and the system starts, you can see the bottom of the screen "error: terminal 'serial' isn't found..' just ignore it as of now and login with the user name and password you provided earlier. it'll launch shell in the /home directory of the user. 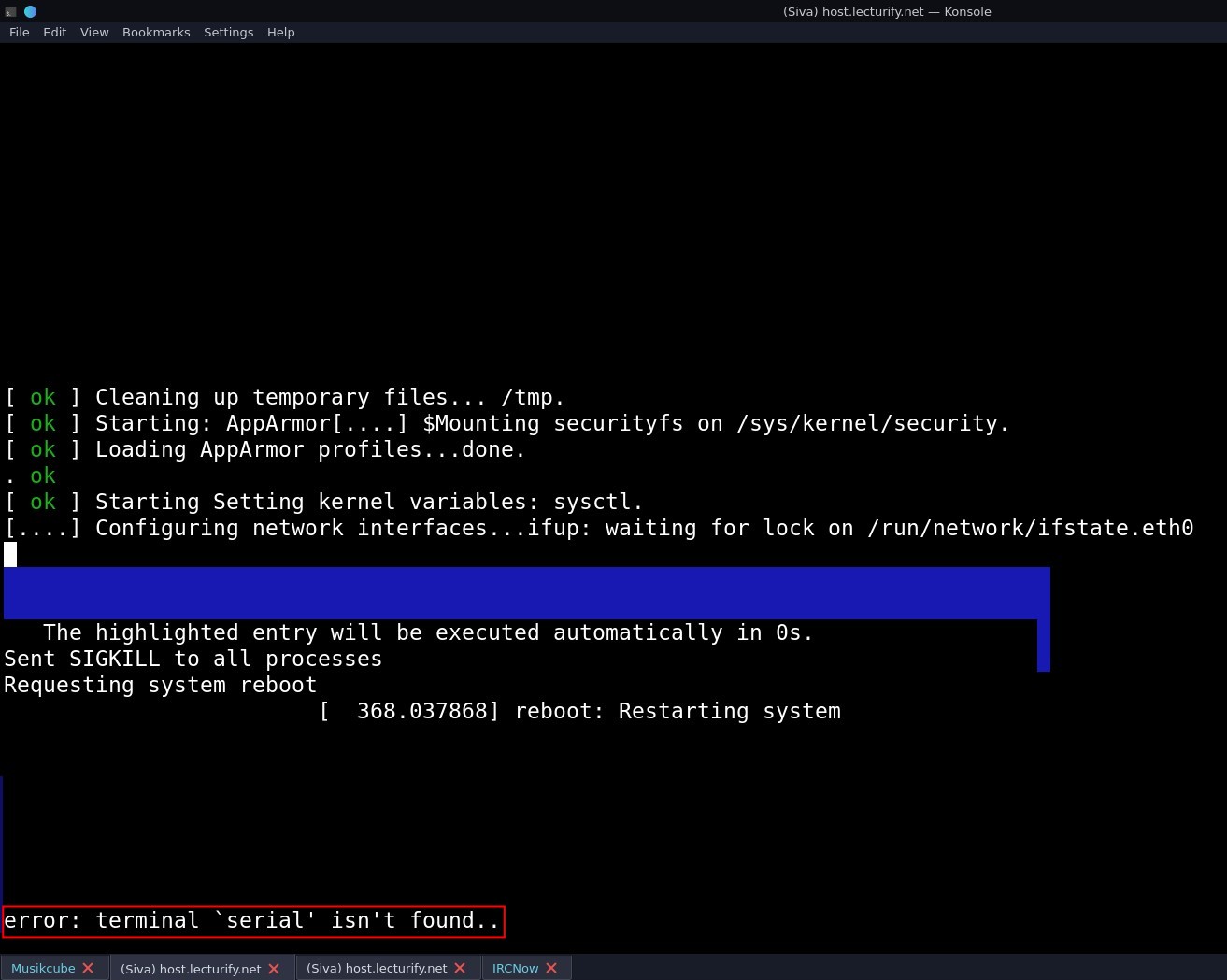
3. Modifying GRUB Configuration
You need to have superuser privileges to do the following, since we don't installed sudo yet, we can't use it so use "su" and enter your "root" password which you set earlier while installation.
$ su $ password: # # nano /etc/default/grub
It'll launch nano text editor with the grub configuration open.
Go to the file end and comment the two options "GRUB_TERMINAL=SERIAL" and "GRUB_SERIAL_COMMAND=serial --unit=0..." lines, it should look like the picture below. 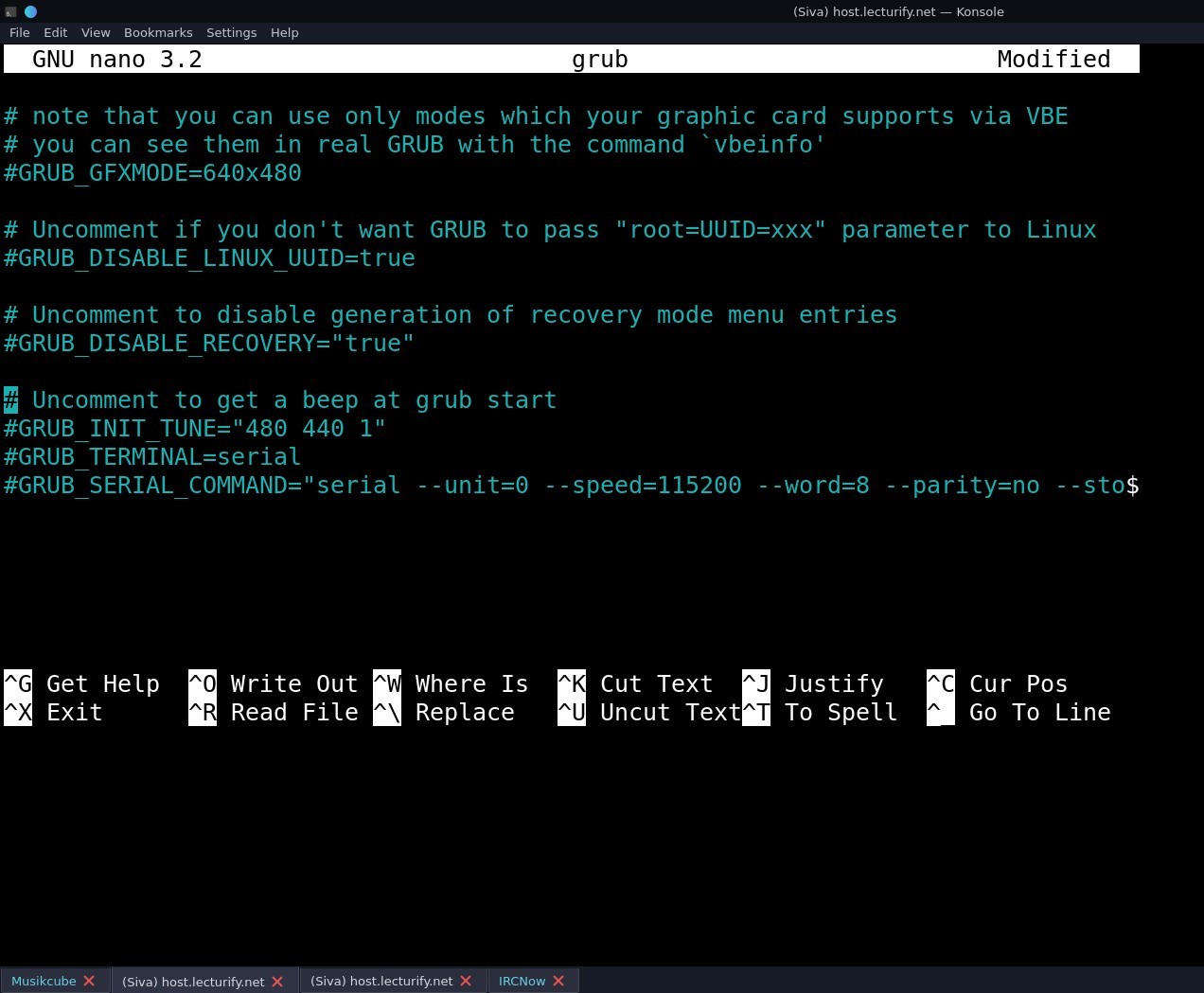
Scroll up on the same file, and uncomment the line "GRUB_TERMINAL=console" (If you don't find the line, just add it manually, without the quotes).
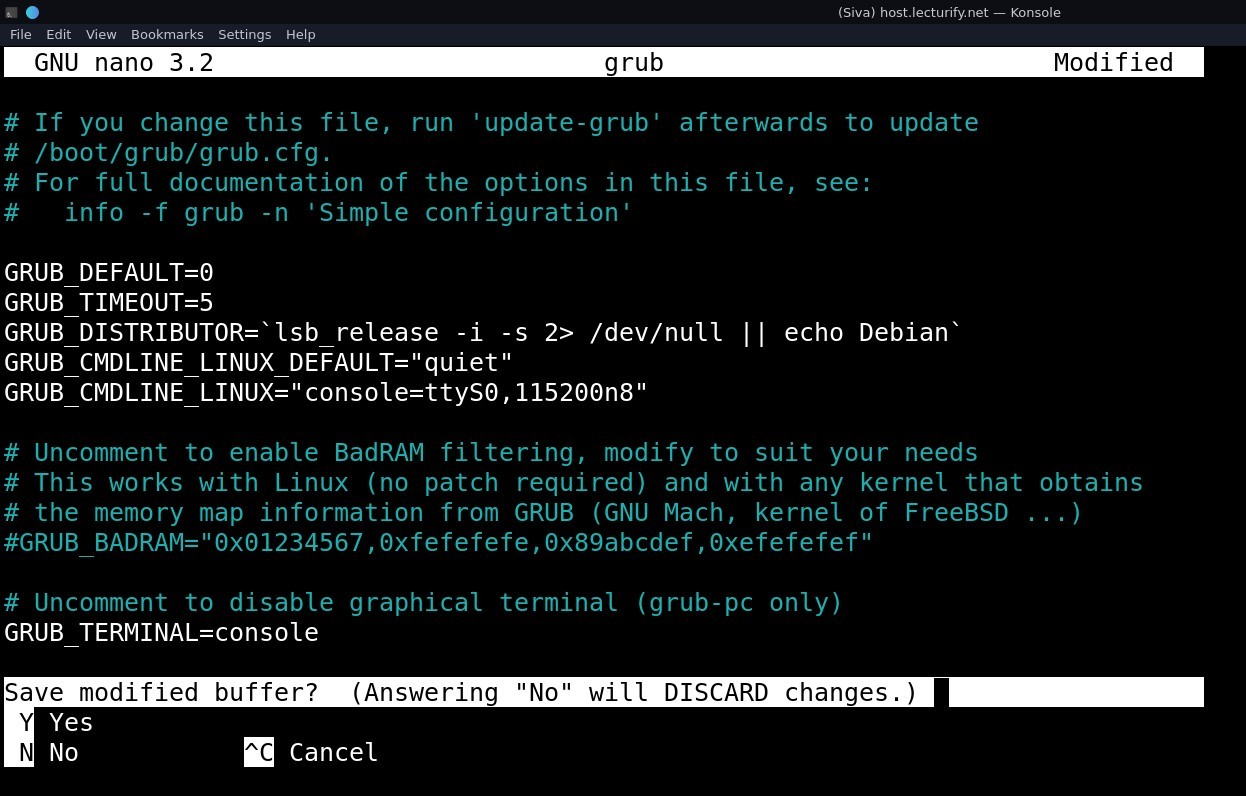
Press "Ctrl + X" , it'll ask "Save Modified Buffer", Make sure you enter "Y" and Press Enter. (Note: Do Not change filename)
Before you update grub, we need to make few changes,
$ export PATH=/usr/sbin/:$PATH
Note: you must type the "$" after the ":"
$ nano ~/.bashrc
and add "export PATH=/usr/sbin/:$PATH" (without quotes) at the end of the file and save it.
now, run update-grub as root user.
# update-grub
if done correctly, you'll get the following texts on screen
Generating grub configuration file ... Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-4.19.0-18-amd64 Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-4.19.0-18-amd64 Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-4.19.0-14-amd64 Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-4.19.0-14-amd64 done
That's it GRUB configuration done, but don't restart yet, we still need to do some tasks.
4. Setting up Cronjob for stable internet connectivity.
You need superuser privileges for this, use su and enter root password.
# crontab -e
the shell now asks you to select an editor to use for crontab editing, choose whatever is comfortable for you
Select an editor. To change later, run 'select-editor'. 1. /bin/nano <---- easiest 2. /usr/bin/vim.tiny
once the crontab opened, type the following very carefully,
@reboot /usr/bin/tmux new -d 'while true; do /bin/ping -i5 38.87.162.1; done' \;
if you choose nano, "Ctrl + X" and "Y" to save the crontab file.
if you choose vim.tiny, make sure you're in command mode and press ":wq" to write and quit the crontab file.
next, install tmux package,
# apt-get install tmux
after installation complete, run the following
# /usr/bin/tmux new -d 'while true; do /bin/ping -i5 38.87.162.1; done' \;
Type carefully on shell, there might be a chance where your terminal 'columns' ends and the typing contents won't show in next line, instead the cursor is shown previous line or same line beginning, just trust your fingers and type carefully and press enter.
Check the tmux window if it is pings correct,
# tmux attach
if ping works fine, press "C-B + D" to detach (C-B = Ctrl+B)
if not, kill the process and repeat the same method above to start a new detached session with ping.
Note: The IP Address shown here is the gateway address of your router, if you are not using "lecturify" host, you should change the IP Address as per your router.
5. Setting up Static IP Address.
Static IP address is important if you use ssh login, and since we don't want to login via console every time, you must have static IP configured.
By default, upon installation, the installer choose DHCP connection and configured it.
Now, you have to find the interface and edit it to be static.
$ ip linkit shows all the interfaces, you can see which interface showing "state UP",
~$ ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast '''state UP''' mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000 link/ether f2:b2:b3:da:eb:07 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
in our case it was "eth0"
now we need to edit the interface file,
you need superuser privileges for the editing it, as root user
open the file "/etc/network/interfaces" using your favorite text editor ,you can see the following line,
"iface eth0 inet dhcp"
change it to, "iface eth0 inet static" (without quotes) and add the following lines with appropriate values
iface eth0 inet static address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 38.87.162.1 dns-nameservers 8.8.8.8 iface eth0 inet6 static address xxxx:xxxx:x:xx:: netmask 48 gateway xxxx:xxxx:x:x::
address should be your IP address for the machine, add netmask as it is, gateway IP should be your router IP (if you using lecturify host machine, the above mentioned IP is correct), add dns nameservers as it it is. Now that's it if you only have IPv4 address, if you want IPv6 configured, add the lines from 'iface eth0 inet6 static' and replace the values for address and gateway as per your IPv6 address.
Save and Exit.
Now, we have to restart network to make the changes take effect, run the following command
# service networking restart
Note: The above command only works, if you've choose the init system as sysvinit , if you've choose others, use appropriate commands as per the init system.
that's it, you can reboot the system now, also use with ssh too.
Note: Do install "sudo" package and setup sudoers file as per your requirement.
:-)
